The ENSNARE project is at the forefront of sustainable building renovation, and the advanced HVAC system (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) being commissioned at the Tartu demonstration site is a prime example of this innovation. This system combines traditional technologies with cutting-edge features to create a system that prioritizes energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Integrating Renewable Energy into HVAC
At its core, the HVAC system relies on a heat pump connected to a radiant floor for heating. What sets it apart is its seamless integration with the ENSNARE solar production system. This system uses solar thermal, photovoltaic, and hybrid panels to prioritize renewable energy. When solar radiation is available, the energy is transferred to a shared tank, ensuring reduced electricity consumption and maximizing sustainability.
Intelligent Ventilation for Healthier Living
The HVAC system also features a smart, window-integrated ventilation setup that adjusts dynamically based on CO2 levels. Operating on three levels, it responds to sensor data to extract stale air and replace it with fresh outdoor air, enhancing indoor air quality and ensuring a healthier environment for the building’s occupants. When indoor air is again of high quality, renovation rates are reduced to the minimum to minimize energy consumption. This system also helps to maintain stable temperatures.

Remote Monitoring and Start-Up
Ensuring the system functions optimally is as critical as its design. The commissioning process involves not only testing the system’s components but also checking data is properly monitored. TECNALIA remotely started the system, collaborating with an Estonian operator on-site. Together, they ensured that key parameters—such as tank temperature, collector temperature, pump status, and internal CO2 levels—were functioning as expected. This approach highlights the project’s ability to combine technical precision with operational practicality, even across borders.
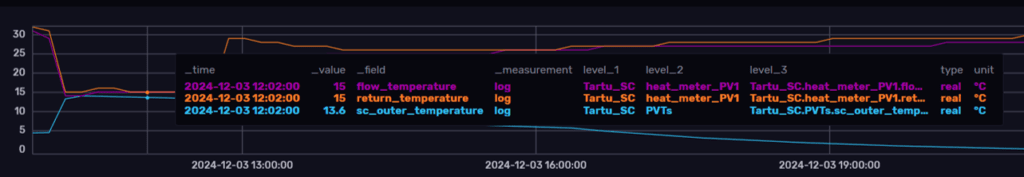
Integration Challenges
The most important challenges involved in the implementation of ENSNARE active strategies is to couple renewable generation with pre-existing HVAC systems. Renewable energies are intermittent, meaning that they don’t produce energy consistently, but must be prioritized when available due to their low carbon footprint. Therefore, an efficient operation and management by means of the digital framework must be ensured, for which the commissioning, proper monitoring and adequate control strategies become key.
A Model for Sustainable Renovation
The Tartu demo site, a social housing site, is a fitting example of how ENSNARE technologies can deliver impactful solutions. By integrating traditional and renewable systems, the project has not only improved energy efficiency but also enhanced comfort and air quality, supporting the building’s social mission.
Looking Ahead
While monitoring data will allow performance assessment to better understand the potential of the system, ENSNARE is proving to be a game-changer for sustainable building renovation. By prioritizing renewable energy, smart automation, and real-time monitoring based on industrialized, modular solutions that provide multifunctional façade modules for façade retrofitting, the project is setting a new standard for residential building retrofits across Europe.

